
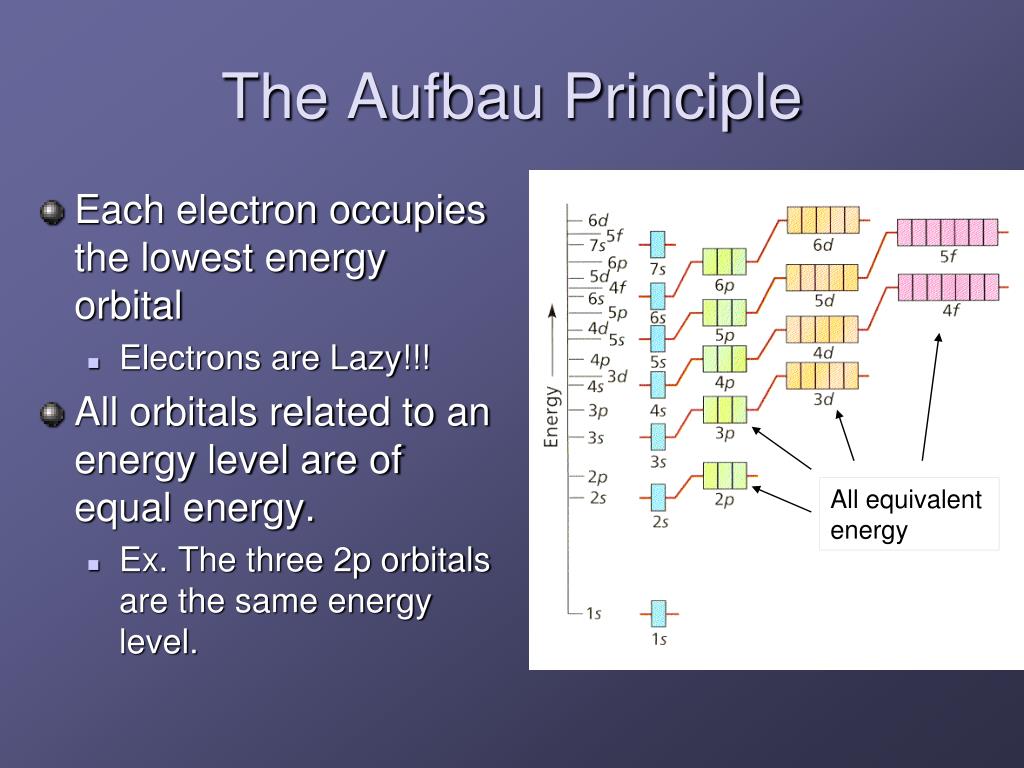
The next orbital is the 2s orbital and holds the next two. An s orbital holds two electrons, so five electrons are left. The first orbital to fill is the 1s orbital. This is all you need to determine the electron configuration of a stable atom of an element.įor example, take the element nitrogen, which has seven protons and therefore seven electrons. F orbitals have seven possible value of m to hold 14 electrons.D orbitals have five possible value of m to hold 10 electrons.P orbitals have three possible value of m to hold six electrons.S orbitals have one possible value of m to hold two electrons.Now that you know the order of orbitals to fill, you need only memorize the size of each orbital. The graphic shows this table and the arrows show the path to follow. Read the chart by running the diagonals starting from 1s.

There are no elements that will need a 6f or 7f shell to fill. Write a column for the d orbitals starting at n=3.( 1p is not an orbital combination allowed by quantum mechanics.) Write a second column for the p orbitals starting at n=2.Write a column of s orbitals from 1 to 8.1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d 7p 8sįortunately, there is a much simpler method to get this order:.Probably the worst way to use the Aufbau principle to figure the fill order of an atom's orbitals is to try and memorize the order by brute force:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
